Unveiling the cell language meaning, we delve into the fascinating world of cellular communication, where cells engage in a complex dialogue to maintain life’s delicate balance.
This intricate language allows cells to send and receive signals, orchestrating a symphony of cellular activities that govern everything from growth and repair to immune responses.
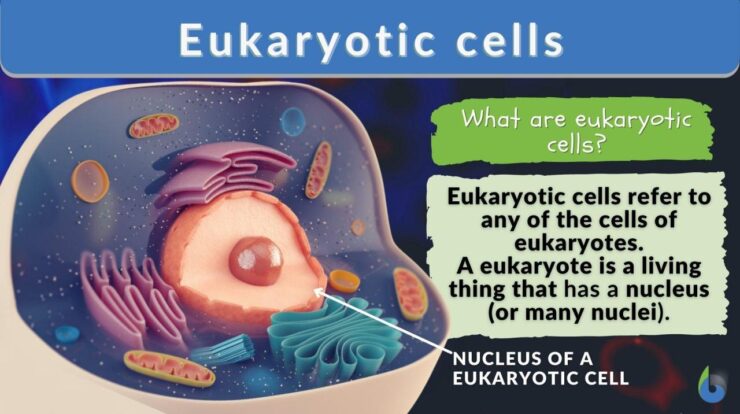
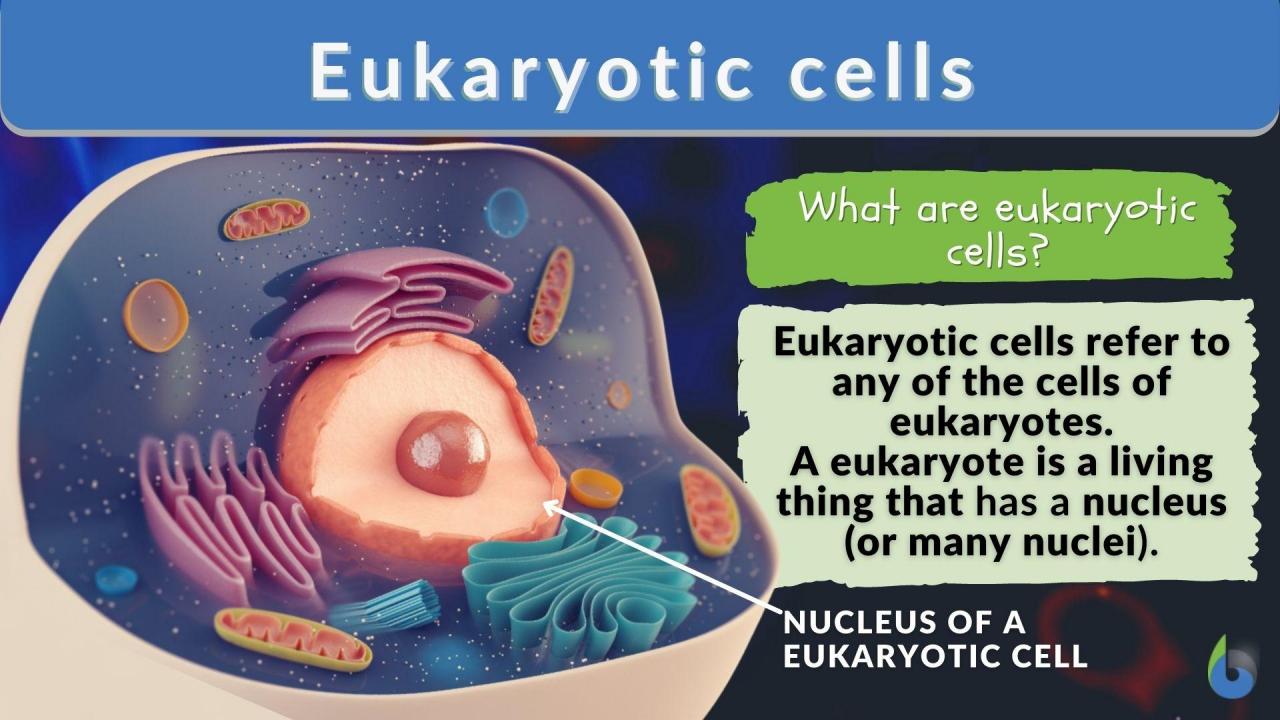
Cell Language Meaning

Cell language refers to the intricate system of communication and signaling that allows cells within an organism to interact and coordinate their functions. It encompasses a diverse array of chemical, electrical, and mechanical signals that enable cells to transmit information, regulate cellular processes, and maintain homeostasis.
Types of Cell Language
There are various types of cell language, each serving specific functions:
- Chemical signals:These involve the release of molecules, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors, that bind to receptors on target cells, triggering specific responses.
- Electrical signals:These involve the movement of ions across cell membranes, creating electrical impulses that can propagate over long distances, as seen in neurons.
- Mechanical signals:These involve physical interactions between cells, such as adhesion molecules and gap junctions, which allow cells to connect and exchange signals directly.
Mechanisms of Cell Language
Cell language is mediated by a complex network of receptors, ligands, and signal transduction pathways:
- Receptors:These are proteins located on the cell surface or within the cell that bind to specific ligands, initiating signal transduction.
- Ligands:These are molecules that bind to receptors, triggering cellular responses.
- Signal transduction pathways:These are intracellular signaling cascades that relay signals from receptors to target molecules within the cell, resulting in specific cellular responses.
Importance of Cell Language, Cell language meaning
Cell language is essential for maintaining homeostasis and coordinating cellular activities:
- Homeostasis:Cell language enables cells to communicate and adjust their functions to maintain a stable internal environment, such as regulating temperature, pH, and nutrient levels.
- Cellular coordination:Cell language allows cells to communicate and coordinate their activities, ensuring that tissues and organs function properly, such as muscle contraction, immune responses, and tissue repair.
Applications of Cell Language
Cell language is a rapidly growing field of research with potential applications in medicine and biotechnology:
- Drug development:Understanding cell language can help identify targets for new drugs that modulate cellular signaling and treat diseases.
- Tissue engineering:Cell language plays a crucial role in tissue development and regeneration, and research is focused on harnessing this knowledge to create functional tissues for transplantation.
Final Wrap-Up
Cell language is not merely a means of communication but a lifeline that connects the microscopic building blocks of life. Understanding its complexities holds immense promise for advancing medicine and unlocking new frontiers in healthcare.
Essential FAQs
What is cell language?
Cell language refers to the diverse ways cells communicate and exchange information to coordinate their activities and maintain homeostasis.
How do cells send signals?
Cells send signals through chemical messengers, electrical impulses, or mechanical forces, which are detected by specific receptors on target cells.
Why is cell language important?
Cell language is crucial for maintaining homeostasis, coordinating cellular activities, and orchestrating complex biological processes.
How is cell language used in medicine?
Cell language research has led to advancements in drug development, tissue engineering, and the understanding of diseases.